5.3 Time Dilation
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how time intervals can be measured differently in different reference frames.
- Describe how to distinguish a proper time interval from a dilated time interval.
- Describe the significance of the muon experiment.
- Explain why the twin paradox is not a contradiction.
- Calculate time dilation given the speed of an object in a given frame.
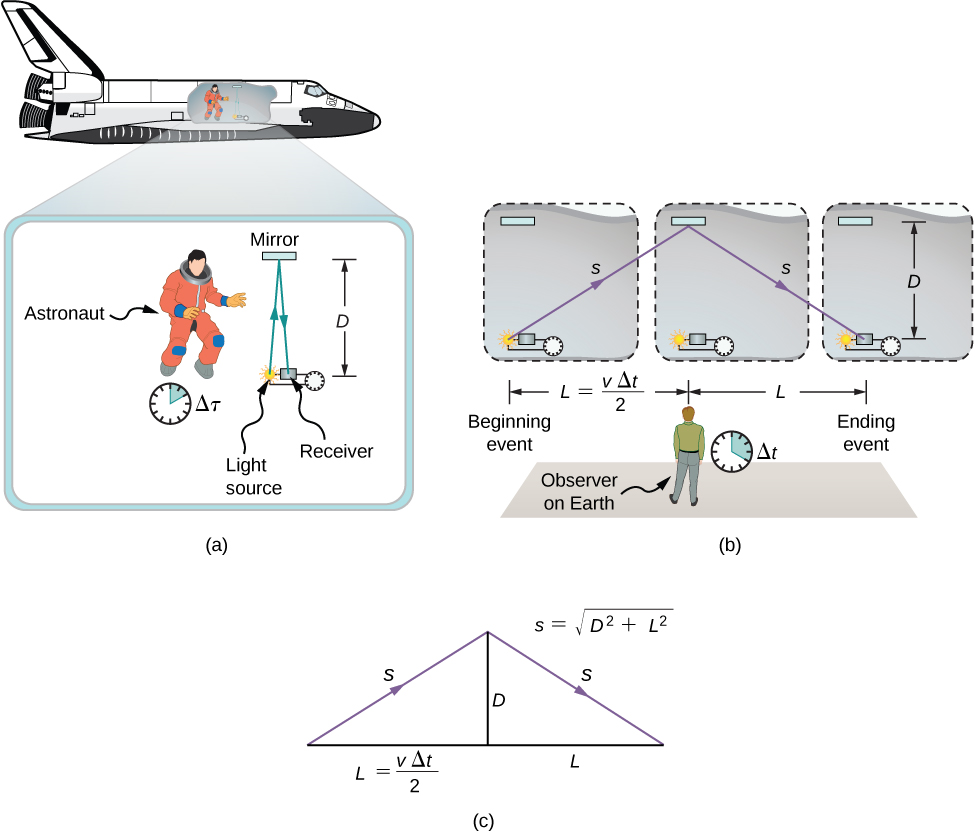
The analysis of simultaneity shows that Einstein’s postulates imply an important effect: Time intervals have different values when measured in different inertial frames. Suppose, for example, an astronaut measures the time it takes for a pulse of light to travel a distance perpendicular to the direction of his ship’s motion (relative to an earthbound observer), bounce off a mirror, and return (Figure 5.4). How does the elapsed time that the astronaut measures in the spacecraft compare with the elapsed time that an earthbound observer measures by observing what is happening in the spacecraft?
Examining this question leads to a profound result. The elapsed time for a process depends on which observer is measuring it. In this case, the time measured by the astronaut (within the spaceship where the astronaut is at rest) is smaller than the time measured by the earthbound observer (to whom the astronaut is moving). The time elapsed for the same process is different for the observers, because the distance the light pulse travels in the astronaut’s frame is smaller than in the earthbound frame, as seen in Figure 5.4. Light travels at the same speed in each frame, so it takes more time to travel the greater distance in the earthbound frame.
Time Dilation
Time dilation is the lengthening of the time interval between two events for an observer in an inertial frame that is moving with respect to the rest frame of the events (in which the events occur at the same location).
To quantitatively compare the time measurements in the two inertial frames, we can relate the distances in Figure 5.4 to each other, then express each distance in terms of the time of travel (respectively either or ) of the pulse in the corresponding reference frame. The resulting equation can then be solved for in terms of
The lengths D and L in Figure 5.4 are the sides of a right triangle with hypotenuse s. From the Pythagorean theorem,
The lengths 2s and 2L are, respectively, the distances that the pulse of light and the spacecraft travel in time in the earthbound observer’s frame. The length D is the distance that the light pulse travels in time in the astronaut’s frame. This gives us three equations:
Note that we used Einstein’s second postulate by taking the speed of light to be c in both inertial frames. We substitute these results into the previous expression from the Pythagorean theorem:
Then we rearrange to obtain
Finally, solving for in terms of gives us
This is equivalent to
where is the relativistic factor (often called the Lorentz factor) given by
and v and c are the speeds of the moving observer and light, respectively.
Note the asymmetry between the two measurements. Only one of them is a measurement of the time interval between two events—the emission and arrival of the light pulse—at the same position. It is a measurement of the time interval in the rest frame of a single clock. The measurement in the earthbound frame involves comparing the time interval between two events that occur at different locations. The time interval between events that occur at a single location has a separate name to distinguish it from the time measured by the earthbound observer, and we use the separate symbol to refer to it throughout this chapter.
Proper Time
The proper time interval between two events is the time interval measured by an observer for whom both events occur at the same location.
The equation relating and is truly remarkable. First, as stated earlier, elapsed time is not the same for different observers moving relative to one another, even though both are in inertial frames. A proper time interval for an observer who, like the astronaut, is moving with the apparatus, is smaller than the time interval for other observers. It is the smallest possible measured time between two events. The earthbound observer sees time intervals within the moving system as dilated (i.e., lengthened) relative to how the observer moving relative to Earth sees them within the moving system. Alternatively, according to the earthbound observer, less time passes between events within the moving frame. Note that the shortest elapsed time between events is in the inertial frame in which the observer sees the events (e.g., the emission and arrival of the light signal) occur at the same point.
This time effect is real and is not caused by inaccurate clocks or improper measurements. Time-interval measurements of the same event differ for observers in relative motion. The dilation of time is an intrinsic property of time itself. All clocks moving relative to an observer, including biological clocks, such as a person’s heartbeat, or aging, are observed to run more slowly compared with a clock that is stationary relative to the observer.
Note that if the relative velocity is much less than the speed of light then is extremely small, and the elapsed times and are nearly equal. At low velocities, physics based on modern relativity approaches classical physics—everyday experiences involve very small relativistic effects. However, for speeds near the speed of light, is close to one, so is very small and becomes significantly larger than
Half-Life of a Muon
There is considerable experimental evidence that the equation is correct. One example is found in cosmic ray particles that continuously rain down on Earth from deep space. Some collisions of these particles with nuclei in the upper atmosphere result in short-lived particles called muons. The half-life (amount of time for half of a material to decay) of a muon is 1.52 μs when it is at rest relative to the observer who measures the half-life. This is the proper time interval This short time allows very few muons to reach Earth’s surface and be detected if Newtonian assumptions about time and space were correct. However, muons produced by cosmic ray particles have a range of velocities, with some moving near the speed of light. It has been found that the muon’s half-life as measured by an earthbound observer () varies with velocity exactly as predicted by the equation The faster the muon moves, the longer it lives. We on Earth see the muon last much longer than its half-life predicts within its own rest frame. As viewed from our frame, the muon decays more slowly than it does when at rest relative to us. A far larger fraction of muons reach the ground as a result.
Before we present the first example of solving a problem in relativity, we state a strategy you can use as a guideline for these calculations.
Problem-Solving Strategy
Relativity
- Make a list of what is given or can be inferred from the problem as stated (identify the knowns). Look in particular for information on relative velocity v.
- Identify exactly what needs to be determined in the problem (identify the unknowns).
- Make certain you understand the conceptual aspects of the problem before making any calculations (express the answer as an equation). Decide, for example, which observer sees time dilated or length contracted before working with the equations or using them to carry out the calculation. If you have thought about who sees what, who is moving with the event being observed, who sees proper time, and so on, you will find it much easier to determine if your calculation is reasonable.
- Determine the primary type of calculation to be done to find the unknowns identified above (do the calculation). You will find the section summary helpful in determining whether a length contraction, relativistic kinetic energy, or some other concept is involved.
Note that you should not round off during the calculation. As noted in the text, you must often perform your calculations to many digits to see the desired effect. You may round off at the very end of the problem solution, but do not use a rounded number in a subsequent calculation. Also, check the answer to see if it is reasonable: Does it make sense? This may be more difficult for relativity, which has few everyday examples to provide experience with what is reasonable. But you can look for velocities greater than c or relativistic effects that are in the wrong direction (such as a time contraction where a dilation was expected).
Example 5.1
Time Dilation in a High-Speed Vehicle
The Hypersonic Technology Vehicle 2 (HTV-2) is an experimental rocket vehicle capable of traveling at 21,000 km/h (5830 m/s). If an electronic clock in the HTV-2 measures a time interval of exactly 1-s duration, what would observers on Earth measure the time interval to be?Strategy
Apply the time dilation formula to relate the proper time interval of the signal in HTV-2 to the time interval measured on the ground.Solution
- Identify the knowns:
- Identify the unknown:
- Express the answer as an equation:
- Do the calculation. Use the expression for to determine from :
Significance
The very high speed of the HTV-2 is still only 10-5 times the speed of light. Relativistic effects for the HTV-2 are negligible for almost all purposes, but are not zero.Example 5.2
What Speeds are Relativistic?
How fast must a vehicle travel for 1 second of time measured on a passenger’s watch in the vehicle to differ by 1% for an observer measuring it from the ground outside?Strategy
Use the time dilation formula to find v/c for the given ratio of times.Solution
- Identify the known:
- Identify the unknown: v/c.
- Express the answer as an equation:
- Do the calculation:
Significance
The result shows that an object must travel at very roughly 10% of the speed of light for its motion to produce significant relativistic time dilation effects.Example 5.3
Calculating for a Relativistic Event
Suppose a cosmic ray colliding with a nucleus in Earth’s upper atmosphere produces a muon that has a velocity The muon then travels at constant velocity and lives 2.20 μs as measured in the muon’s frame of reference. (You can imagine this as the muon’s internal clock.) How long does the muon live as measured by an earthbound observer (Figure 5.5)?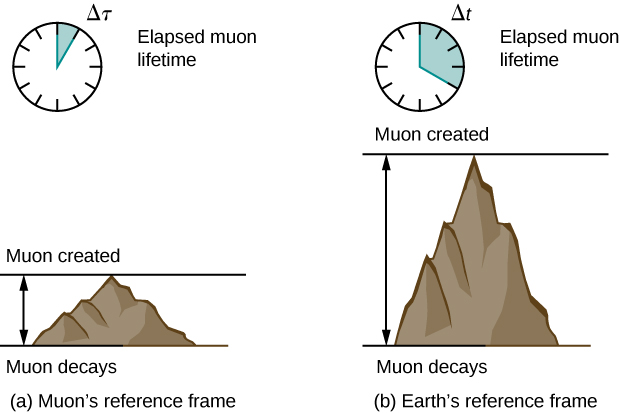
As we will discuss later, in the muon’s reference frame, it travels a shorter distance than measured in Earth’s reference frame.
Strategy
A clock moving with the muon measures the proper time of its decay process, so the time we are given is The earthbound observer measures as given by the equation Because the velocity is given, we can calculate the time in Earth’s frame of reference.Solution
- Identify the knowns:
- Identify the unknown:
- Express the answer as an equation. Use: with
- Do the calculation. Use the expression for to determine from Remember to keep extra significant figures until the final answer.
Significance
One implication of this example is that because at 95.0% of the speed of light the relativistic effects are significant. The two time intervals differ by a factor of 3.20, when classically they would be the same. Something moving at 0.950c is said to be highly relativistic.Example 5.4
Relativistic Television
A non-flat screen, older-style television display (Figure 5.6) works by accelerating electrons over a short distance to relativistic speed, and then using electromagnetic fields to control where the electron beam strikes a fluorescent layer at the front of the tube. Suppose the electrons travel at through a distance of from the start of the beam to the screen. (a) What is the time of travel of an electron in the rest frame of the television set? (b) What is the electron’s time of travel in its own rest frame?
Strategy for (a)
(a) Calculate the time from Even though the speed is relativistic, the calculation is entirely in one frame of reference, and relativity is therefore not involved.Solution
- Identify the knowns:
- Identify the unknown: the time of travel
- Express the answer as an equation:
- Do the calculation:
Significance
The time of travel is extremely short, as expected. Because the calculation is entirely within a single frame of reference, relativity is not involved, even though the electron speed is close to c.Strategy for (b)
(b) In the frame of reference of the electron, the vacuum tube is moving and the electron is stationary. The electron-emitting cathode leaves the electron and the front of the vacuum tube strikes the electron with the electron at the same location. Therefore we use the time dilation formula to relate the proper time in the electron rest frame to the time in the television frame.Solution
- Identify the knowns (from part a):
- Identify the unknown:
- Express the answer as an equation:
- Do the calculation:
Significance
The time of travel is shorter in the electron frame of reference. Because the problem requires finding the time interval measured in different reference frames for the same process, relativity is involved. If we had tried to calculate the time in the electron rest frame by simply dividing the 0.200 m by the speed, the result would be slightly incorrect because of the relativistic speed of the electron.Check Your Understanding 5.2
What is if
The Twin Paradox
An intriguing consequence of time dilation is that a space traveler moving at a high velocity relative to Earth would age less than the astronaut’s earthbound twin. This is often known as the twin paradox. Imagine the astronaut moving at such a velocity that as in Figure 5.7. A trip that takes 2.00 years in her frame would take 60.0 years in the earthbound twin’s frame. Suppose the astronaut travels 1.00 year to another star system, briefly explores the area, and then travels 1.00 year back. An astronaut who was 40 years old at the start of the trip would be 42 when the spaceship returns. Everything on Earth, however, would have aged 60.0 years. The earthbound twin, if still alive, would be 100 years old.
The situation would seem different to the astronaut in Figure 5.7. Because motion is relative, the spaceship would seem to be stationary and Earth would appear to move. (This is the sensation you have when flying in a jet.) Looking out the window of the spaceship, the astronaut would see time slow down on Earth by a factor of Seen from the spaceship, the earthbound sibling will have aged only 2/30, or 0.07, of a year, whereas the astronaut would have aged 2.00 years.
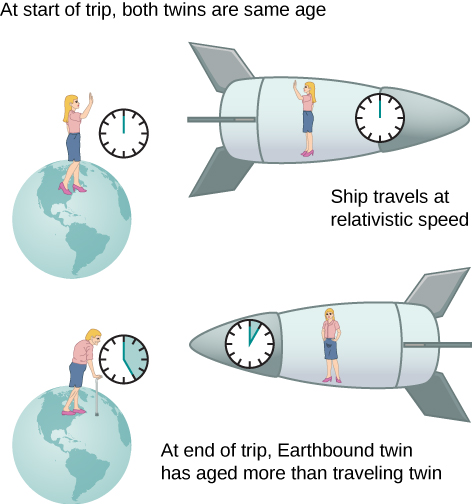
The paradox here is that the two twins cannot both be correct. As with all paradoxes, conflicting conclusions come from a false premise. In fact, the astronaut’s motion is significantly different from that of the earthbound twin. The astronaut accelerates to a high velocity and then accelerates opposite to the motion to view the star system. To return to Earth, she again accelerates and decelerates. The spacecraft is not in a single inertial frame to which the time dilation formula can be directly applied. That is, the astronaut twin changes inertial references. The earthbound twin does not experience these accelerations and remains in the same inertial frame. Thus, the situation is not symmetric, and it is incorrect to claim that the astronaut observes the same effects as her twin. The lack of symmetry between the twins will be still more evident when we analyze the journey later in this chapter in terms of the path the astronaut follows through four-dimensional space-time.
In 1971, American physicists Joseph Hafele and Richard Keating verified time dilation at low relative velocities by flying extremely accurate atomic clocks around the world on commercial aircraft. They measured elapsed time to an accuracy of a few nanoseconds and compared it with the time measured by clocks left behind. Hafele and Keating’s results were within experimental uncertainties of the predictions of relativity. Both special and general relativity had to be taken into account, because gravity and accelerations were involved as well as relative motion.
Check Your Understanding 5.3
a. A particle travels at and lives when at rest relative to an observer. How long does the particle live as viewed in the laboratory?
b. Spacecraft A and B pass in opposite directions at a relative speed of An internal clock in spacecraft A causes it to emit a radio signal for 1.00 s. The computer in spacecraft B corrects for the beginning and end of the signal having traveled different distances, to calculate the time interval during which ship A was emitting the signal. What is the time interval that the computer in spacecraft B calculates?