Chapter 2
Check Your Understanding
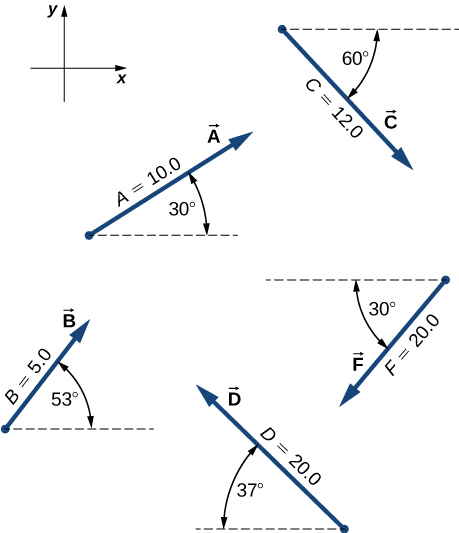
2.1
a. not equal because they are orthogonal; b. not equal because they have different magnitudes; c. not equal because they have different magnitudes and directions; d. not equal because they are antiparallel; e. equal.
2.15
or, equivalently, , and the direction is into the page; or, equivalently, , and the direction is out of the page.
Conceptual Questions
21.
a. , b. or , c. , d. , e. , f. , g. left side is a scalar and right side is a vector, h. , i. , j.
Problems
55.
, D = 360.5 yd, north of east; The numerical answers would stay the same but the physical unit would be meters. The physical meaning and distances would be about the same because 1 yd is comparable with 1 m.